The multidomain approach provides answers in the search for new forms of resilience in a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous world (VUCA-world). This approach has to be understood comprehensively and holistically, including various areas such as technology, culture, economy, science and society. Accordingly, this term which originally had a military connotation, should not be understood solely within security policy contexts. Multidomain increasingly has a strategic component within economy, society and politics.
Nonetheless, in this article we focus on the military environment, where the concept of joint forces is related to the multidomain approach, meaning the battle of combined arms. It’s a matter of how the different service branches are coordinated and jointly directed. The evolution of this joint concept can be split into the following four generations:
- Joint 1.0
Historically, the combined arms consisted of the joint deployment of infantry, artillery and cavalry, which was subsequently supplemented and replaced by armored vehicles.
- Joint 2.0
Over time, warfare evolved beyond ground forces. Thus, the next evolutionary step consisted of the interconnection of ground, air and naval forces. The establishment of the so-called Forward Air Controller, which can request, coordinate and lead the deployment of close air support in an ongoing battle from the ground, can be highlighted as an example.
- Joint 3.0
Within the realm of the third generation, joining ground, air and naval force is expanded by including space, cyberspace and electromagnetic spheres. In this context, Network-Centric Warfare (NCW) became a central term. Therein, various C4ISTAR concepts led to a technological and process-related dynamization of the sensor, intelligence, command and effect cycles. The communication and interconnectedness of systems is to be ensured and the operations command has to be networked accordingly. Thereby, transmitting and processing of data’s getting more and more important (although in a purely technical sense). The U.S. armed forces founded the U.S. Cyber Command or the sixth service branch, the U.S. Space Force, as a manifestation of this technological development.
- Joint 4.0
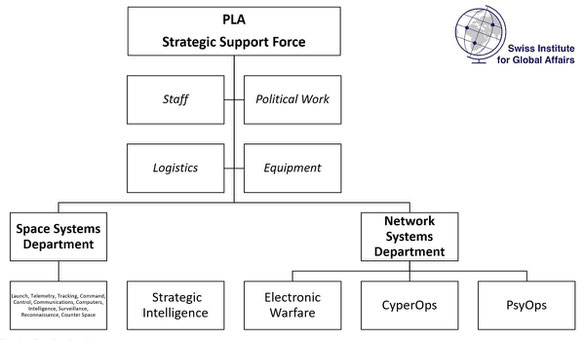
Joint 4.0 will be the coronation of this development. Thereby, the individual departments and service branches will no longer be only loosely connected, but united strategically and dynamically. For example, this will additionally include domains like intelligence, psychological operations, information and influence operations, legal and media warfare. Consequently, information is not anymore understood within technological categories, but furthermore as a symbolic, informational and narrative category. Especially, the creation of the Chinese Strategic Support Force (SSF) and the associated strategic consolidation of the branches of information, cyber, electronic warfare, space and intelligence have already been described as an innovative and future-oriented approach. This is about information-driven conflicts and wars. Information dominance, information superiority but also information shields are therefore essential elements of a dynamized joint thinking of the future.
According to the concept of Joint 4.0, SIGA recommends upgrading, integrating and dynamizing intelligence competences and components as an information related operational force. Including military music as operative communication tool could unleash unused potential for instance. In addition, command support and logistics should increasingly be conceptualized and deployed as active, operational elements. For only the overall system can guarantee cross-domain defense and security in a modern environment.
Dr. Remo Reginold & Urs Vögeli